How Does the Exhaust System Work?
The exhaust system in your car removes dangerous gases produced during combustion, which is essential for fuel economy, the environment, and your safety. The exhaust system "cleans up" the gases before they are released into the environment in addition to preventing harmful pollutants like hydrocarbons, nitrogen oxides, and carbon monoxide from entering the cabin.At the very end of the exhaust system, a muffler reduces noise levels by directing sound waves through a variety of pipes and holes, cancelling out a lot of the sound waves from your engine.
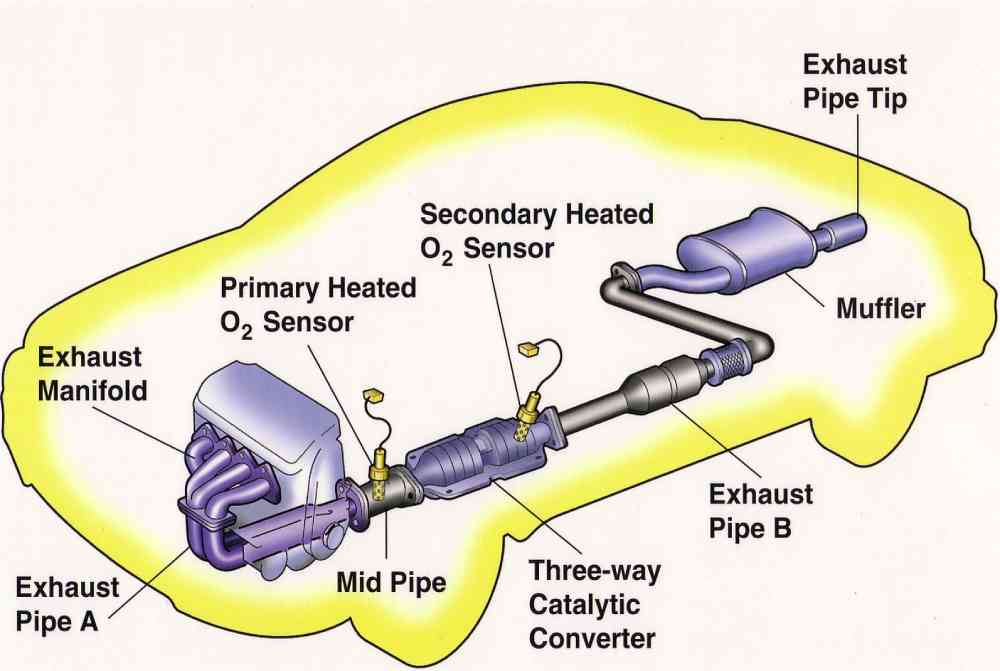
What Does A Full Exhaust System Include?
Before we take a detailed look at all components of your exhaust system, it helps to remember how many different parts make up this seemingly simple setup. So, to illustrate the inner workings of your car here’s a list of components you can expect to see in a stainless-steel full exhaust system or say a complete exhaust system:
- Catalytic converter
- Exhaust manifold
- Exhaust pipes
- Front muffler
- Front pipe
- Gaskets
- Rear muffler
- Heat shields
- Rear pipe
- Resonator
- Oxygen sensor
- Hangers
- Diesel particulate filter DPF (diesel cars)
- Tailpipe
What Are The Basic Parts Of The Exhaust System?
While modern exhaust systems contain dozens of parts, many of these are (technically) nonessential or perform auxiliary duties, such as heat shields that help protect the underside of your car. Out of all the parts in your exhaust system, the following parts are the most important:
Exhaust Manifold
First and foremost is the exhaust manifold: typically made of cast iron or fabricated tubing, the manifolds sometimes incorporate the catalyst and connect to the engine at the exhaust ports with flange connectors. Exhaust gases leaving the engine first travel through the exhaust manifold. The manifold collects the exhaust gases from the individual ports in the engine’s cylinder head, then routes those gases to the rest of the exhaust system. Engines with a ‘V’ or flat configuration have two exhaust manifolds (one for each bank of cylinders), whereas inline or straight engines have just one manifold.
Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter is an emissions control device that converts harmful exhaust gases into water, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen. Some catalytic converters (or CATs for short) are integrated into the exhaust manifold, whereas others are attached to the vehicle’s exhaust pipe. It’s also worth noting that some cars have just one catalytic converter, while others have as many as four.
Oxygen Sensor
The oxygen sensor (O2 sensor) is a small probe that measures the oxygen in your exhaust system and sends data to your ECU, helping to monitor and improve fuel efficiency. Modern vehicles have both upstream and downstream oxygen sensors. Upstream oxygen sensors are located before the catalytic converter, while downstream sensors are located after the converter. The engine computer, which is often referred to as the powertrain control module (PCM), uses data from the upstream oxygen sensor to regulate the engine’s fuel mixture. Meanwhile, the PCM primarily uses the signal from the downstream oxygen sensor for monitoring the health of the catalytic converter.
Muffler
Last but not least, mufflers are typically fitted near the end of exhaust systems and (as its name implies) muffle the noise of your engine to abide by noise restriction legislation. While they may look simple on the outside, mufflers use a precise configuration of pipes and baffles to create an echo chamber that cancels out sound waves rather than just filtering them out.
Exhaust Pipes
Various exhaust pipes connect the parts of the exhaust system together. The pipes are often made from aluminized or stainless steel to protect against rust and corrosion.
Tailpipe/Exhaust Pipe Tip
The tailpipe, or say exhaust pipe tip, is the final link in the exhaust system—it routes the exhaust gases, which have been cleaned up by the catalytic converter, away from the vehicle and into the atmosphere.
Keep Your Exhaust System Efficient
As the old saying goes, prevention is better than a cure. Fortunately, there are various ways to maintain your exhaust system, which range greatly in cost and convenience. To help keep your exhaust in working order for longer, consider the following factors and techniques:
- Wear and tear/Corrosion – rain, snow and grit can corrode your exhaust over time, so check for wear and tear more often if you drive through muddy/sandy areas often.
- Fuel Purity – Impurities in your fuel can clog up your exhaust and cat, reducing engine performance over time, so think about the higher octane options when you fill up next.
- Active regeneration – by driving at high speeds for longer periods, you can burn off carbon deposits in your catalytic filter, a process known as active regeneration.
- Carbon cleaning – many garages offer carbon cleaning services that clean your exhaust from the inside out, removing lots of impurities and carbon buildup.
Here are the tips on how to clean your exhaust system.
Where To Buy Parts For Your Exhaust System
There’s no doubt that the exhaust system is essential to your vehicle, and keeping all its parts in tip-top shape is essential for smooth, clean driving. If you find any leaks, obstructions, or loose components among its parts, it might be time for a change. The last thing you want is for these issues to affect your vehicle’s emissions. Luckily, getting parts for your exhaust system is easy at CNRautoparts.



Validate your login